Advantage of Pandas.
Practical Use of Pandas.
from pandas import DataFrame import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np a=np.array([[4,8,5,7,6],[2,3,4,2,6],[4,7,4,7,8],[2,6,4,8,6],[2,4,3,3,2]]) df=DataFrame(a, columns=['a','b','c','d','e'], index=[2,4,6,8,10]) df.plot(kind='bar') # Turn on the grid plt.minorticks_on() plt.grid(which='major', linestyle='-', linewidth='0.5', color='green') plt.grid(which='minor', linestyle=':', linewidth='0.5', color='black') plt.show()
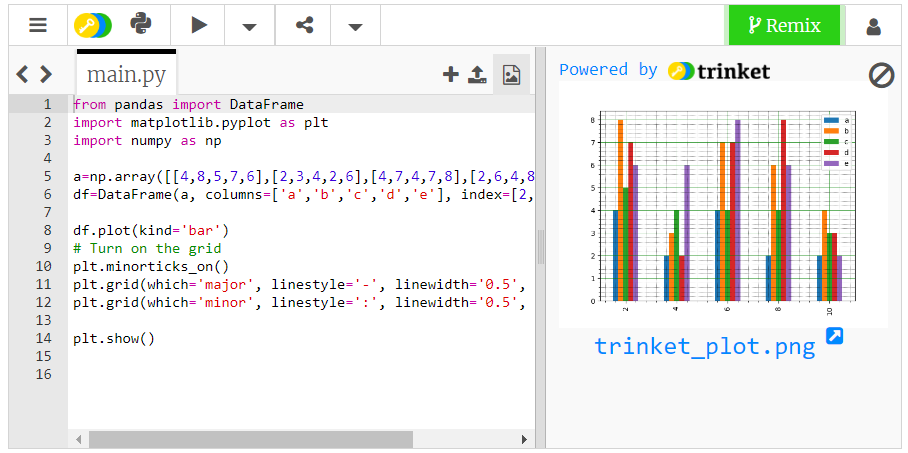
Commonly used Pandas methods.
Creating Data Frames/Series from scratch.
Pandas Data Frame can be created from a Python Dictionary. The keys in a dictionary becomes a column header and the array values for the key becomes the rows for that header.
import pandas as pd
# declare a dataframe
df = pd.DataFrame(
{
"Name": [
"Braund, Mr. Owen Harris",
"Allen, Mr. William Henry",
"Bonnell, Miss. Elizabeth",
],
"Age": [22, 35, 58],
"Sex": ["male", "male", "female"],
}
)
print(df)
On the other hand, Pandas Series can be created either from a Python Dictionary or derived from an existing Pandas Data Frame.
import pandas as pd
# (1) declare a series from a dictionary
Ages1 = pd.Series(
{
"Age": [22, 35, 58],
}
)
print(type(Ages1))
print(Ages1)
print("----------------------------------------")
# (2) declare a series from a previously declared dataframe
Ages2 = df["Age"]
print(type(Ages2))
print(Ages2)
Pandas Data Frame and Series can also be created from a Python List. However, the resulting dataframe/series will be missing the column names.
import pandas as pd
# declare a dataframe
df = pd.DataFrame(
[
["Braund, Mr. Owen Harris",22,"male"],
["Allen, Mr. William Henry",35,"male"],
["Bonnell, Miss. Elizabeth",58,"female"],
],
)
print(df)
print("----------------------------------------")
# declare a series
ds = pd.Series(
[22, 35, 58],
)
print(ds)
Alternatively, add an additional parameter (columns for dataframe and name for series) that defines the column names in the dataframe/series declaration statement.
import pandas as pd
# declare a dataframe
df = pd.DataFrame(
[
["Braund, Mr. Owen Harris",22,"male"],
["Allen, Mr. William Henry",35,"male"],
["Bonnell, Miss. Elizabeth",58,"female"],
],
columns=["Name","Age","Sex"]
)
print(df)
print("----------------------------------------")
# declare a series
ds = pd.Series(
[22, 35, 58],
name="Name"
)
print(ds)
Import/Export Data Frames/Series from/to external sources.
Usually the data source for Data Frame and Series are imported from text files e.g. CSV.
import pandas as pd # declare a dataframe from a remote file filepath="https://archive.org/download/misc-dataset/titanic.csv" df_titanic = pd.read_csv(filepath) print(type(df_titanic)) print(df_titanic[["PassengerId","Survived","Pclass"]])
Conversely, the Data Frame can be exported back to CSV file. Besides CSV, Data Frame can be exported to several other formats i.e. using methods to_dict(), to_excel(), to_json(), to_numpy() etc. (Read further: How do I read and write tabular data?).
import pandas as pd # declare a csv targetfilepath targetfilepathcsv="titanic.csv" df_titanic.to_csv(targetfilepathcsv) # declare a csv targetfilepath targetfilepathxls="titanic.xls" df_titanic.to_excel(targetfilepathxls)
Preview Data.
import pandas as pd # declare a dataframe from a remote file filepath="https://archive.org/download/misc-dataset/titanic.csv" df_titanic = pd.read_csv(filepath) print(df_titanic.head()) # the output shows head data(default 5 rows)
import pandas as pd # declare a dataframe from a remote file filepath="https://archive.org/download/misc-dataset/titanic.csv" df_titanic = pd.read_csv(filepath) print(df_titanic.tail()) # the output shows tail data(default 5 rows)
import pandas as pd # declare a dataframe from a remote file filepath="https://archive.org/download/misc-dataset/titanic.csv" df_titanic = pd.read_csv(filepath) print(df_titanic[500:505]) # the output shows a slice of data
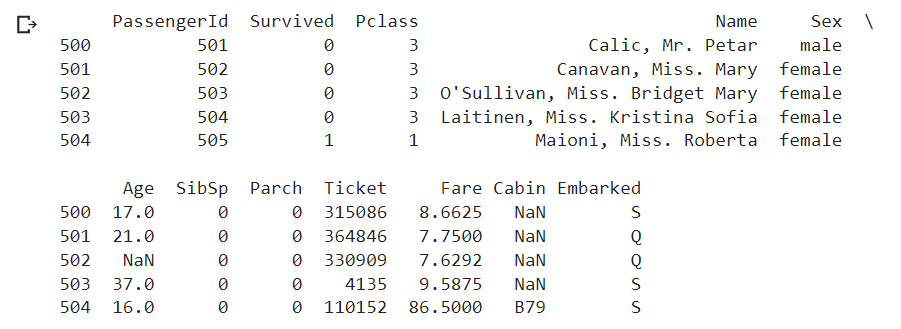
Preview Meta Data.
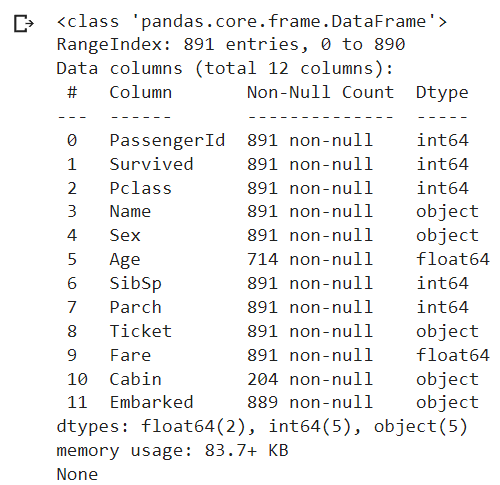
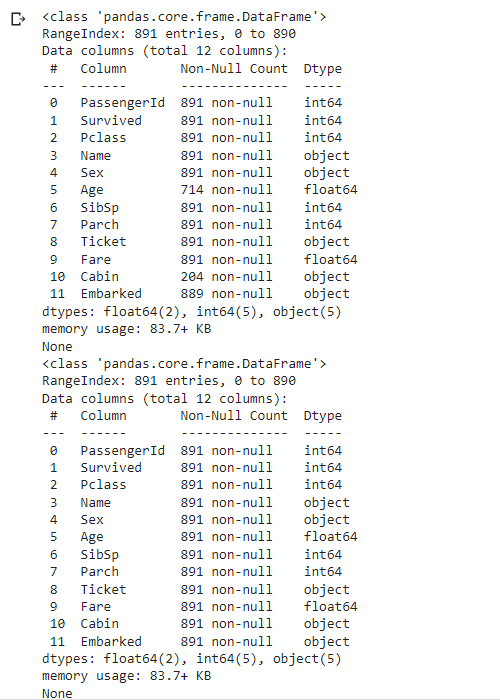
import pandas as pd # declare a dataframe from a remote file filepath="https://archive.org/download/misc-dataset/titanic.csv" df_titanic = pd.read_csv(filepath) print(df_titanic.info()) # the output shows: # df data type # range index # column description
Preview Data Description.
import pandas as pd # declare a dataframe from a remote file filepath="https://archive.org/download/misc-dataset/titanic.csv" df_titanic = pd.read_csv(filepath) print(df_titanic.shape) # the output shows: # (row size/column sizes)
import pandas as pd # declare a dataframe from a remote file filepath="https://archive.org/download/misc-dataset/titanic.csv" df_titanic = pd.read_csv(filepath) print(df_titanic.describe()) # the output shows: # descriptive statistics of the data
Selecting Specific Row/Column of Data.
import pandas as pd # declare a dataframe from a remote file filepath="https://archive.org/download/misc-dataset/titanic.csv" df_titanic = pd.read_csv(filepath) # using loc i.e. select by label location print(df_titanic.loc[df_titanic['Age'].isna()==False,['Age']])
import pandas as pd # declare a dataframe from a remote file filepath="https://archive.org/download/misc-dataset/titanic.csv" df_titanic = pd.read_csv(filepath) # using iloc i.e. select by integer location print(df_titanic.iloc[list(df_titanic.Age.isna()==False),[5]])
Dropping Data.
import pandas as pd
# declare a dataframe from a remote file
filepath="https://archive.org/download/misc-dataset/titanic.csv"
df_titanic = pd.read_csv(filepath)
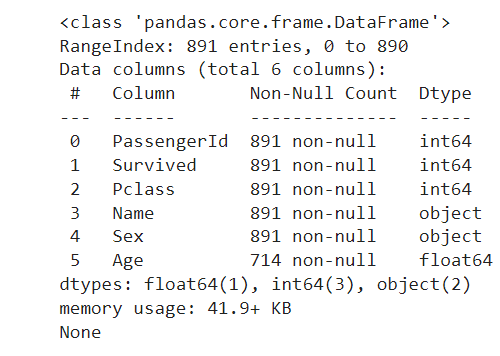
df_titanic = df_titanic.drop(columns=['SibSp', 'Parch', 'Ticket',
'Fare','Cabin','Embarked'])
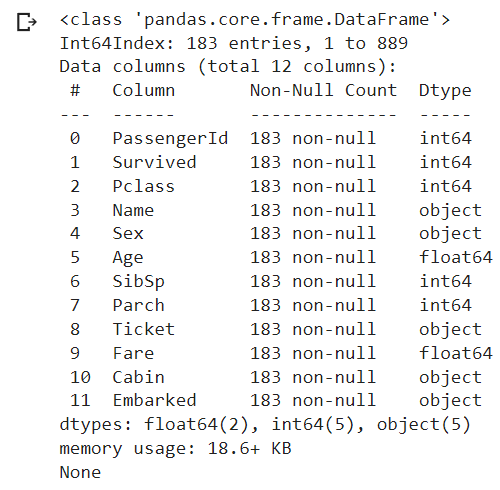
print(df_titanic.info())
# the output shows:
# remaining 6 columns
# (the other 6 columns have been dropped)
import pandas as pd # declare a dataframe from a remote file filepath="https://archive.org/download/misc-dataset/titanic.csv" df_titanic = pd.read_csv(filepath) df_titanic = df_titanic.dropna() print(df_titanic.info()) # the output shows: # remaining 183 rows # (other 714 rows with missing values have been dropped)
Imputing Data.
import pandas as pd # declare a dataframe from a remote file filepath="https://archive.org/download/misc-dataset/titanic.csv" df_titanic = pd.read_csv(filepath) print(df_titanic.info()) df_titanic.fillna(0, inplace = True) print(df_titanic.info())
import pandas as pd # declare a dataframe from a remote file filepath="https://archive.org/download/misc-dataset/titanic.csv" df_titanic = pd.read_csv(filepath) age_mean=int(df_titanic['Age'].mean()) print(age_mean) # replacing missing values with mean value df_titanic.fillna(age_mean, inplace = True) # select the first 10 rows and column Age print(df_titanic.loc[:10,['Age']])









![[what] Lambda (Anonymous Function) In Python](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhFcCMnHmDuefUzrRAsSR6u9oQDNYMzJn5mGIM3DcFKwiLkTM1zYLb_ydhamlqwxG94dJFMDG6ioBKkXYB4U4VSei1mKX3D3DZ_ic2Q1woqNM-Zfn1ZZzZygwLo8f-V2S15Fgrtg58DVesegNSBlLjunDWfnmf4c48wBrUIb66gXxoFf-GCmCkB9hdu/w72-h72-p-k-no-nu/lambda-1.jpg)
![[what] SciPy (Scientific Computing in Python)](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEga6AJY1_FY6eEacD62tgn-vTle0J3Um2KS32RUfHbFMZ6pqPDZ0I0FI95Cq1zi4iR2R1S5YfvFnquvb4idQity36zVX36YKJsIFYcQDYneZsm7jt5Bg1A5FpGiSph2z7fg1fxLoaZtJqltfvn228XW5r3JdR8jMwZbmFDisq0AG2UYMmhBdDxmYQE1/w72-h72-p-k-no-nu/scipy.jpg)
![[what] Pandas (Panel Data Analysis) In Python](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgi8Yz3ogVcc0z6P2cf_LA3E4VqesuI9KdNK-yCf_hcLESIjXx4R7_5YrJxfrgLVE1iDfRv2thgSbn5aggVkkRAhUS_kFZHzWDFFrmtxxeO66TKruIDO5JEHfRzID7th801uJYuwJ9GkBhxPhiAk7LCfJh7HGh53YfXsGxVELvTzRIPuYQCl-xDF4-f/w72-h72-p-k-no-nu/panel-data.jpg)
![[what] Iterables and Iterators In Python](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjalQDpgm5KJqMGVa5bivgzsMGDDx0qNbJ-SUZbxMHdX6Mw8618tzHhRjZvx6HEeYHxr5_XHEsI9wQk4OfqtOmUBVBDEJA5kTlH-KYD-EX7yI5DU1GDfkwaaHzp3SbpcD6RfltrpQ-67mqEZTyLh10ZuRj_PNoH5XwOL8Ji5G3keuPYKLDM4xP2FOkC/w72-h72-p-k-no-nu/iterables-iterators.jpg)
![[what] Basic Program Control Structures In Python](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgfp5UTw1HRWFs6CvOYl7Rup9YEjBIWYyCPtudMp2IXIKF_N-v_pfj0cesSk6-oDOLQFhOtiP3-V3OdPad38NftngX0MUmWJTXmplySQvE8TcfXqYf_6qMUzzH9S1zINbD2NrYBNNVjMdxEv8URMIrt3s_J31MOjrcJK-DpnrxOK47YzQdcaCe1pxF9/w72-h72-p-k-no-nu/01-hello-world.png)
![[how] Organize Text Data Using Pandas (Python Data Analysis Library)](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEju8-3O2Gin-OBBav3EUAQwP6m_7svhPzPgYoPkyzK-pcbPWkZjJtDbNBLUPmRyPiB9aB6lAteLH0VNrvmm1qmqPVkp8DoxMBQCNO6Ho1_fdX-OAv9QYn_xU9OmHKCpqsvqgI7yUlLZwCRgdTtIl76Sw8zhkTgzvnjTAT0zxbEC5_H57R66raT9mY3-/w72-h72-p-k-no-nu/pandas-dataframe.jpg)
![[how] Connect Colab To Google Sheet](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjOwMYfzIxcAL36yTXWGC3JSykf-LlEZlLgE83aSVYL0AWll6cTQCg-TejFtmzy77kCrOfFWhAMKkAaI5XlfOQa2jrVFrJEa5lVg0-AUuInnoVB-tpy8olM3UFq5U8Etq9j1CbBOp-oopqC9ZXMWaQZDaVFH1uitp8jE5sgqJHlmRYg2HehKcP_v5Kd/s840/keyboard2.jpg)

![[get-started] Python For Beginners](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjmS6FFThm5ApijpmeGWIvjoEAS8yU1HgGQ8gJ8pn19WbJJvVPY7HT1mKwFdKDIyi1WqnNdML9Gg5yzs0ZU8Ql8mskxP9eHYOEJ3qrL9LDjQJvbNXVSJ-fJXBlNpDR4UPeIshr5VE86VRJlSdrwwgm8JtXA3Km1BWALtIBssD4uFsWJhUdFNzh0pvrt/w72-h72-p-k-no-nu/python-getting-started.jpg)
![[what] Python Map, Filter and Reduce Functions](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhxthbUIItcyDXW1GJ6gHRvaUL7LyeA2m7GsBgI0Gb4y-VBcHmcPFkuZPfSxLhrffJwyiWpQqGibQQRhCJM71ir_OLIJ9wB1gs-U-ssiW-xh_gry6A2wHGCRSSfnjedcyGTGDNcQlfnAxZSwVQ4cCIDUHa6iTQRVWaZl8Qbz3B2LAUTFhzQ2Jvmgu4o/w72-h72-p-k-no-nu/map-filter-reduce.jpg)

0 Comments